Question 1
a. Given that
Ø = 2x2 yz3 determine ∇.∇∅
b. Find the first four terms of the Maclaurin’s series expansion for f(x) = sin2x
Solution
a) Solving divergence of a gradient we integrate the expression twice
∇∅ = (∂2x2 yz3)/∂x I + (∂2x2 yz3)/∂y j + (∂2x2 yz3)/∂z k
=4xyz3 i + 2x2 z3 j + 6x2 yz2 k.
∇.∇∅ = (∂4xyz3)/∂x I + (∂2x2 z3)/∂y j + (∂6x2 yz2)/∂z =4yz3 + 12x2yz
Note; the divergence of a gradient is always a Scalar Quantity
b. Firstly you have to find from 1st – 7th of f(x) and equate it to zero(0):
f(x)= sin 2x f(0)= sin 2(0)= 0
fi(x)= 2 cos2x fi(0)= 2 cos2(0)= 2
fii(x)= -4 sin2x fii(0)= -4 sin2(0)=0
fiii(x)= -8 cos2x fiii(0)= -8 cos2(0)=-8
fiv(x)= 16 sin2x fiv(0)= 16 sin2(0)=0
fv(x)= 32 cos2x fv(0)= 32 cos2(0)=32
fvi(x)= -64 sin2x fvi(0)= -64 sin2(0)=0
fvii(x)= -128 cos2x fvii(0)= -128 cos2(0)=-128
f(x)=f(0)+xf’ (0)+x2/2! f” (0)+x3/3! f”’ (0)+
x4/4! fiv (0) + x5/5! fv (0) + x6/6! fvi (0)+ x7/7! fvii (0)
f(x)=0 + 2x+x2/2! (0)+x3/3! (-8) + x4/4! (0)+ x5/5! (32)+ x6/6! (0)+ x7/7! (-128)
Using the Maclaurin’s series Equation you’ll arive at;
f(x)=2x – [(8x3)/(1×2×3)] + [(32x5)/(1×2×3×4×5)] – (128x7)/(1×2×3×4×5×6×7)
f(x)=2x – (4x2)/3 + (4x5)/15 – (8x7)/315
Question 2
a. Verify the convergence or otherwise of the given GP
2 + 6 +18 + 54 +…..
b. Given that A = 3y2zi -2x2yj- xyz2k find the curl of A at (1,-2,1)
Solution
a. Applying the formular of GP
Sn=(a(1 – rn))/(1-r) r<1 Sn=(a(1 – rn))/(r – 1) r>1
Sn=(2(1-3n))/(3-1) = (2(1-3n))/2= (1-3n)
Sn=(1-3n ) n→∞
Sn=1 – 3∞=1- ∞ = -∞
The series is a divergence series. As n tends to infinity 3n will become a very large number making the series Divergence
b. Note The curl of a function is always a vector quantity
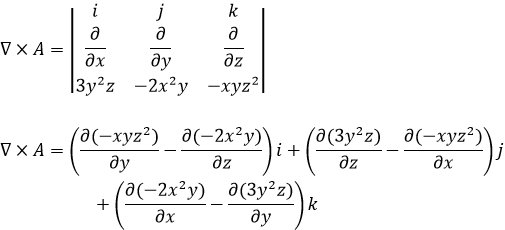 = -xz2i +(3y2 +xz2)j + (-4xy -6yz)k
= -xz2i +(3y2 +xz2)j + (-4xy -6yz)k
at A(1,-2,1)
= -(1)(1)2i + (3(-2)2 + 1(1)2)j + (-4(1)(2) -6(-2)(1))
The curl of A = -i +13j +k
Question 3
Evaluate
∬sA ̅.n ̅ds, where A ̅=18zi-12j+3yk
S is the part of the plane 2x + 3y + 6z =12 Given that the projected surface S of A is in the plane xy and the projection points to z-axis direction
Solution
The formula for surface integral :
∬A.n ̅ds A=18zi-12j+3yk
S : 2x+3yz+6z=12 x- y plane z-axis direction
∬A ̅ n ̂ds n ̂=∇f/|∇f| ds=dxdy/|n.k|
∬F n ̂ dxdy/|n.k|
f=2x+3y+6z-12
∇f=∇(2x+3y+6z-12)=2i+3j+6k
|∇f|=√(22+32 +62 ) =√49 =7
Therefore we have;
n ̂=∇f/|∇f| = (2i+3j+6k)/7
n.k=1/7(2i+3j+6k)
n.k = 1/7×6 = 6/7
A.n ̂ = (18zi-12j+3yk) . (1/7 (2i+3j+6k))
=(36z-36+18y)/7
From the equation of the surface (z axis direction)
z=(12-2x-3y)/6
Substituting z in the above equation becomes;
A.n ̂=1/7 (36(12-2x-3y)/6 – 36 + 18)
=1/7 (72 – 12x – 18y – 36 + 18y)
=1/7 (36-12x)
∬Fn ̅ds =∬1/7 (36-12x) dxdy/6 ×7 remember n.k=7/6
∬6(6-12x) dxdy/6
∬(6-12x)dxdy
To find the limit of the integration, take the x-y plane at which z=0 so that you can have: 2x+3y =12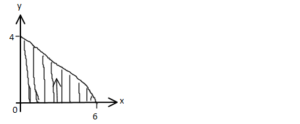
From the equation at x=0 y=4
From the equation at y=0 x=6
X varies from x=0 to x=6
Y varies from y=0 t0 y = (12-2x)/3
∫06∫0((12-2x)/3) (6-2x)dxdy
∫06(6-2x)dx (y) ((12-2x)/2) ¦ 0
∫06(6-2x)dx ((12-2x)/2)
∫06(24-12x+4/3 x2 )dx=24
Question 4
a. Given that w = z2 + 4 determine dw/dz at the point (2,3).
b. given that z1=1 + j2, z2 = 4 – j3, z3 = -2 +j3 and z4 = -5 -j find.
i. z1 + z2 – z3 in polar form
ii. z1 z2 z3in exponential form
iii. (z1 + z3) /(z2 +z4) in cartesian form
Solution
a.
z = x+ iy
z2 = (x+iy)2 = x2+ 2xyi – y2
w = x2+ 2xyi – y2 +4
w = x2– y2 +4+ 2xyi
w= u +iv
u = x2– y2 +4 v = 2xy
Differentiating u and v with respect to both x and y;
∂u/∂x=2x ∂u/∂y=-2y.
∂v/∂x=2y ∂v/∂y=2x
∂w/∂z = ∂u/∂x + j∂v/∂x = ∂v/∂y –j ∂u/∂y
=2x+j2y = 2x – j(-2y)= 2x + j2y
Thus w = 2x + j2y
b.
z1=1 + j2, z2 = 4 – j3, z3 = -2 +j3 and z4 = -5 -j
i. in polar (r, θ)
z1 +z2 +z3 = (1 + j2) + (4 – j3) – ( -2 +j3 )
=(1+4+2) +j(2-3-3)
=7 –j4
r=√(72+42 )=√65
θ=tan-1(-4/7)= -29.7 ≈-30o
-4 and 7 is on the 4th quadrant
θ=360 – 30=330o
(√65 , 330o)
ii. in exponentail Z = rejθ
z1 z2 z3= (1+j2)(4-j4)(-2+j3)
=(4-j3+8j+6) (-2+j3)
=(4+j5+6) (-2+j3)
=(10+j5) (-2+j3)
=-20 +j30-j10-15
=-35 +j20
r=√((-35)2+(20)2 )=√1625 = 40.3
θ=tan-1(20/-35)= -29.7≈ 30o
θ=180 – 30= 150o
z=40ej150
Z = 40ej150
Thus z1 z2 z3 in exponetial form is equal= 40ej150
iii.
(z1+z2)/(z2-z4 ) = [(1+j2)+(-2+j3)]/[(4-j3)—(-5-j) ]=[(-1+j5))/((9-j2) ]
Multiplying by the conjugate of (9-j2)
=[(-1+j5)/(9-j2) ] × [(9+j2)/(9+j2)]
= (-9-j2+j40-10)/(92+4)
=(9+j30-10)/(81+4) = (-1+j30)/85=-1/85 + j 30/85
=(-1/85 + j 30/85)
Question 6
a. using De’alambert ratio test prove on the convergence or otherwise of the series below
1 + 1/3 + 1/9 + 1/27 + 1/81 + …….
b. find (1+i)8 using Demoiver’s theorem
Solution
a.
D’alembert ratio test
k=U(n+1) /Un
k<1 convergent
k>1 divergent
1/3o +1/31 +1/32 +1/33 +1/34
Therefore Un=1/3n U(n+1) =1/3(n+1)
Applying the D’Alembert formula
K=1/3(n+1) ÷1/3n
=1/3(n+1) × 3n/1= 3n/3(n+1)
Applying law of indices
=3(n-(n+1)) = 3(-1)
k=1/3 the series is convergent since k<1
b.
Applying Demoiver’s Theorem:
(1+i)8 a=1 b=1 n = 8
Zn=rn (cosnθ + sinnθ )
r=√(a2+b2 ) = √(12+12 )=√2
θ=tan-1(1/1) =45° = π/4\
Z = (√2)(cosn(π/4)+sinn(π/4))
Substituting the value of n = 8
Z8 = (√2 )8 (cos8(π/4)+sin8(π/4))
Z8=16(cos2π + sin2π )
cos2π = -1 and sin2π = 0
Z8 = 16( -1 + 0 ) =-16
Therefor: Z8 = -16
Question 7
Find the Fourier expansion to represent
f(x)= π – x for 0<x<2π
Solution
Using the formula of Fourier Series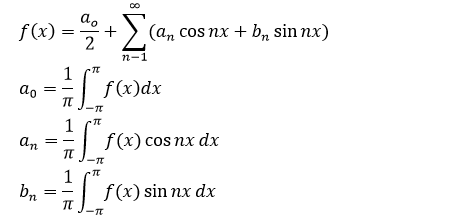
Finding the value of ao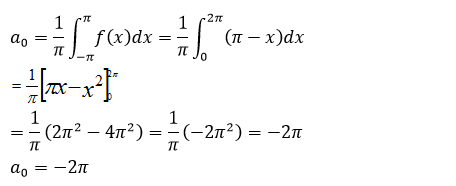
Now finding the value of an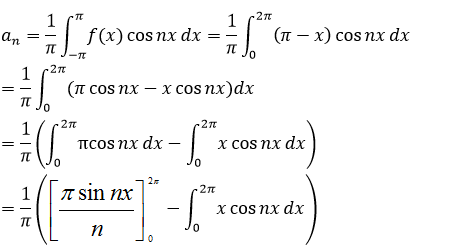 Applying integration by part;
Applying integration by part;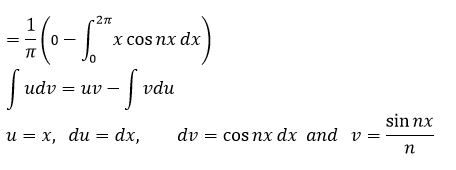
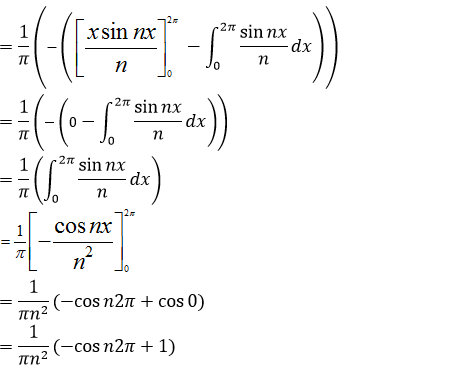
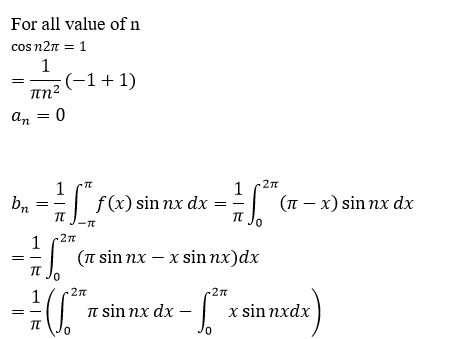
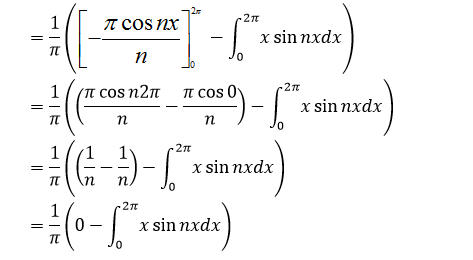
Apply integration by part;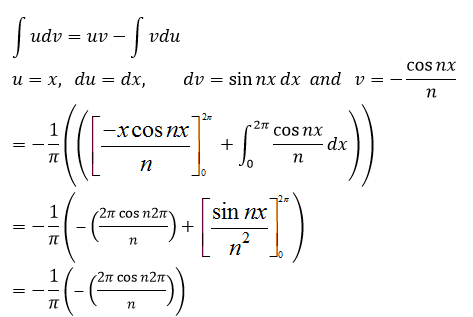
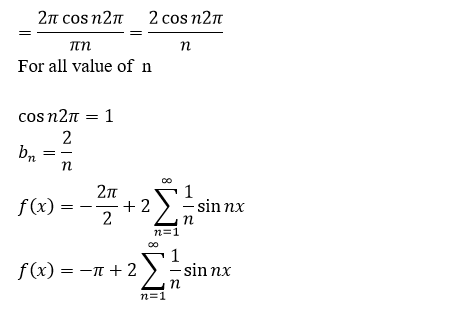
Question8
a. Evaluate the following if
Z1 = 1 – j3, Z2 = -2 + j5 and Z3 = -3 –j4
i) Z1Z2 in (a + jb)
ii) form Z1/Z3 in polar form
iii) Z1Z2/ (Z1 +Z2)
b) Find Z1Z2Z3
Solution
a)
i) Z1Z2 = (1-j3) (-2 + j5)
= -2 +j5 +j6 -j215
=-2 +j5 +j6 + 15
Z1Z2 = 13 +j11
ii) Z1/Z3 = (1-j3)/(-3-j4)
Multiplying through by the conjugate of ( -3 + j4)
= (1-j3)/(-3-j4) × (-3+j4)/(-3+j4)
= (-3+ j4+j9-j212)/(32+42 )
=9/25 + j13/25
=0.36 + j 0.52
Polar form (r,θ) r=√(x2+y2) θ = tan-1(y/x)
r=√(0.362+ 0.522 ) = √0.4 = 0.6
θ=tan-1(0.52/0.36) = 60°
Z1/Z3 = (0.6, 60°)
ii) Z1 + Z2 = (1-j3) + (-2+j5)
= (1-2) + j(-3 +5)
= -1 +2j
Z1 + Z2 = -1 +2j Z1Z2 =13 + j11
(Z1 Z2)/(Z1+Z2 ) = (13 + j11)/(-1+2) × (-1-2)/(-1-2)
(-13-j26-j11-j2 22)/(-12+22)
=(9-j37)/5 = 9/5 – j 37/5
= 1.8 – j7.4
Z = (x + jy) ( Complex form)
Z = ( r, θ) ( Polar form)
Z = re-jθ (Exponential form)
r=√((1.8)2+(7.4)2 ) =√25.33 = 5.03
θ=tan-1(7.4/1.8) = 76.3°
Z=5e-j76.33
Question 9
a. A = 3x2y – 2xyzj + yxk Find
∇× A̅ at (1,-1,1)
b. Verify the convergence or otherwise of the GP below
1+ 1/3 +1/9 + 1/27 +1/81 +⋯
Solution
a) Finding the Curl of the vector

= ( z – 2xy)i + (0 – 0)j + (2yz -3x2)z
= ( z – 2xy)i + (2yz -3x2)z
At (1, -1, 1)
=(1 -2(1)(-1))i + (2(-1) (1) – 3 (1)2)z
=(1+2)i + (-2-3)z
=3i – 5z
b) a=1, r = 1/3÷1 = 1/3×1 = 1/3
Sn = (a(1 – rn))/(1-r)
Sn = 1(1-(1/3)n ) / (1- 1/3)
Sn=((1- (1/3)n )) / (2/3)
Sn = (1- (1/3)n ) ÷ 2/3
Sn= (1 – (1/3)n ) × 3/2
as n→∞ (1/3)n= 0
Sn=(1-0) x 3/2 = 2/3
Sn=3/2 Therefore it is Convergence
Question 10
a) Expand f(x) = e7x using Maclaurin’s series expansion
b) Find ∇∅= 1/|r| where r = xi + yj + zk
Solution
a)
f(x)= e7x f(0)= e0=1
fi(x)= 7e7x fi(0)= 7e0=7
fii(x)= 47e7x fii(0)= 47e0=47
fiii(x)= 343e7x fiii(0)= 343e0=343
fiv(x)= 2401e7x fiv(0)= 2401e0=2401
fv(x)= 16807e7x fv(0)= 16807e0=16807
f(x)=f(0) + xf’’ (0) + x2/2! f’’(0) + x3/3! f’’’(0)+⋯
f(x)=1 + (x × 7) + (x2/2! × 49) + (x3/3! × 343) + (x4/4! × 2401) + (x5/5! × 16807)
f(x)=1 + 7x + (49x2)/2 + (343x3 )/6 +(2401x4)/24 + (16807x5)/120
b)
r ̅= xi + yj + zk
|r ̅ |=√((xi)2+(yj)2+(zk)2 ) = √(x2 + y2+z2 )
|r ̅ |=(x2+y2+z2 )1/2
∅=1/| ̅r| =1/(x2+y2+z2 )1/2 =(x2+y2+z2 )-1/2
∇∅ = (d(x2+y2+z2 )-1/2/dx) i + (d(x2+y2+z2 )-1/2/dy) j + (d(x2+y2+z2 )-1/2/dz) k ……(i)
Now to find (d(x2+y2+z2 )-1/2/dx)
let s =(x2+y2+z2 )-1/2 and u = x2+y2+z2
du/dx = 2x du/dy = 2y du/dz = 2z
s = u-1/2
ds/du=-1/2 u-3/2
ds/dx = ds/du × du/dx = -1/2 u-3/2 × 2x = -x u-3/2
Therefore (d(x2+y2+z2 )-1/2/dx) = ds/du × du/dx
= -x u-3/2
Inserting the value of u = x2+y2+z2
(d(x2+y2+z2 )-1/2/dx) = -x (x2+y2+z2 ) -3/2 …………………….(ii)
Applying the same approach to (d(x2+y2+z2 )-1/2/dy)
ds/dy = ds/du × du/dy = -1/2 u-3/2 × 2y = -y u-3/2
Thus (d(x2+y2+z2 )-1/2/dy) = -y (x2+y2+z2 ) -3/2 …………..(iii)
Also (d(x2+y2+z2 )-1/2/dz) = -1/2 u-3/2 × 2z = -z u-3/2
(d(x2+y2+z2 )-1/2/dz) = -z (x2+y2+z2 ) -3/2 …………………….(iv)
Inserting equation (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) in equation (i)
∇∅= -x (x2+y2+z2 ) -3/2 i -y (x2+y2+z2 ) -3/2 j -z (x2+y2+z2 ) -3/2 k
∇∅= – (x2+y2+z2 ) -3/2 (xi + yj+ z)
Question 11
a) Expand f(x) = In(x-2) as a series of ascending power of x
b) If F =6xyi + y2 j Evaluate ∫c Fdr for C at (0,0) to (1,2)
Where C is the curve in the xy plane define by y = 2x
Solution
a) f(x)=f(0) + xf’’ (0) + x2/2! f’’(0) + x3/3! f’’’(0)+⋯
f(x)=In(x-2) f(0)=In(-2)
f’(x)=1/(x-2) f’(0)=-1/2
f’’(x)=(-1)/(x-2)2 f’’(0)=-1/4
f’’’(x) = 2/ (x-2)3 f’’’(0)=-1/4
fiv (x)= -6/(x-2)4 fiv (0)=-3/8
fv (x)=24/(x-2)5 fv (0)=-3/4
b)
w= ∫c Fdr r ̅ = xi+yj dr ̅ =dxi + dyj
∫(6xyi+y2 j)(dxi + dyj)…….(i)
y=2x dy/dx=2 dy=2dx
Inserting the value of y and dy in equation (i)
∫(6x(2x)dx + (2x)2 . 2dx)
∫(12x2 dx + 8x2 dx)
∫20x2 dx
C at (0,0) to (1,2) Using the limit of x 0 to 1
∫0120x2 dx
=(-20x3/3) limit of 0 to 1
=(20(1)3)/3)=20/3
w= =20/3
Question 12
a) Give the w = (3z – j)2 determine dw/dz at the point (2,3)
b) Does the series 2/3 + ¾ + 4/5 +5/6 + ….. converge or diverge
Solution
a)
dw/dz = du/dx + j dv/dx = dv/dy- j du/dy
du/dx + j dv/dx = dv/dy- j du/dy
Thus du/dx = dv/dy and dv/dy = -du/dy
W= (3z – j)2 = (3z – j) (3z – j)
W = 9z2 –j 3z –j3z + j2
W = 9z2 –j6z -1……. (i)
Recall z = x+ jy
Z2= (x + jy)(x+ jy) = x2 + j2xy – y2
Substituting the value of z and z2 in eqn (i)
W = 9(x2 + j2xy – y2) – j6(x + jy) – 1
W = 9x2 + j18xy –9 y2 – j6x + 6y -1
W = (9x2 –9 y2 + 6y -1) + j(18xy– 6x)
Note that W = u + jv Therefore;
u = 9x2 –9 y2 + 6y -1 and v = 18xy – 6x
du/dx = 18x du/dy = -18y + 6
dv/dx = 18y – 6 dv/dy = 18x
Using the formula du/dx + j dv/dx = dv/dy – j du/dy
= 18x + j(18y – 6) =18x – j(-18y + 6)
= 18x +j(18y -6) = 18x + j(18y -6)
dw/dz = 18x + j(18y -6)
dw/dz at (2, 3)
dw/dz = 18(2) + j(18(3) – 6)
dw/dz = 36 +j48
b) Finding the equation of the series 2/3 + ¾ + 4/5 +5/6 + …..
we get: Sn=(n+1)/(n+2)
limn→∞ Sn=(∞+1)/(∞+2) = ∞/∞
Sn=undetermined
The series is divergence
Question 13
Find the Fourier series for the function shown. consider one cycle between x = -π and π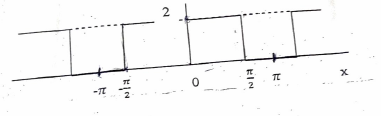
Solution



 considering different integers for the value of n
considering different integers for the value of n
If n is even![]()
If n is odd but having the value of 1, 5, 9…..![]()
If n is odd but having the value of 3, 7, 11…..


Disclaimer
This entire solution may not be 100% accurate, any mistake or typo found should be reported to SmartBukites Management through the following email [email protected] »
All the custom solutions are written for individual research and reference ONLY. SmartBukites does not promote plagiarism in any form and firmly believes that Student will use the solutions models in their individual efforts.
Do you have a Question to Ask?
SmartBukites have a Facebook Group which allows everyone to ask, answer and seek academic help. At SmartBukites, we believe Smart approach to Education will go along way in easing human academic struggle.
Click the link to join now!!! https://web.facebook.com/groups/675122219621351
